 Extended School Year (ESY) is a provision under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) that ensures students with disabilities who need them receive educational services beyond the regular school year in an effort to prevent significant regression and support the maintenance of critical skills necessary for a student’s academic progress.
Extended School Year (ESY) is a provision under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) that ensures students with disabilities who need them receive educational services beyond the regular school year in an effort to prevent significant regression and support the maintenance of critical skills necessary for a student’s academic progress.
Section 300.106 of IDEA requires districts to provide ESY services that are “provided to a child with a disability (a) beyond the normal school year, (b) in accordance with the child’s IEP; and (c) at no cost to the caregivers of the child.” These services must be provided “only if a child’s IEP Team determines, on an individual basis… that the services are necessary for the provision of FAPE (Free and Appropriate Public Education) to the child.”
ESY may include additional instruction in specific areas like reading, math, language skills, addressing individual student needs. This personalized approach focuses on areas where the student may experience regression without continuous support. This instruction is not designed to provide new information or teaching, but merely to maintain the student’s current level of performance.
Therapies such as speech-language therapy, occupational therapy, or physical therapy may be provided during ESY to maintain progress and prevent regression. These services are tailored to the unique needs of each student, ensuring a holistic approach to development. Continued support for behavioral interventions and strategies also helps students maintain positive behavior patterns.
ESY is not the appropriate environment for compensatory services. Compensatory services, addressing gaps or skill loss, should be dealt with separately from ESY, as each serves a distinct purpose in supporting the student’s educational journey. While ESY focuses on prevention and maintenance, compensatory services target specific areas of skill development that may require additional support.
ESY Qualification
The IEP team conducts a thorough review and assessment of a student’s current performance levels and factors that may contribute to regression during breaks around March/April for schools that typically end their regular school year in May. Objective data on the students progress and regression patterns should be collected throughout the year to inform the decision-making process. This can include noting any behavior or academic regressions observed after three-day weekends, fall break, and holidays.
The IEP team, including caregivers, engages in collaborative decision making, reviewing the collected data and assessing each student’s unique needs. This ensures that ESY services align with the specific requirements of the student, maximizing their educational benefits. Written notice of the decision is provided via Prior Written Notice (PWN), explaining the reason for granting or denying ESY services. Transparent communication is crucial, allowing caregivers to actively participate in their child’s educational journey.
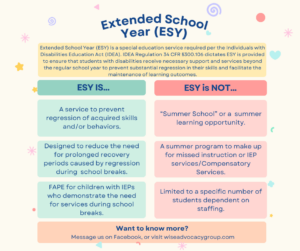
Extended School Year (ESY) IS:
- Based only on the individual student’s specific critical skills that are crucial to his/her overall educational progress as determined by the IEP committee.
- Designed to maintain student mastery of critical skills and objectives represented on the IEP and achieved during the regular school year.
- Designed to maintain a reasonable readiness to begin the next year.
- Based on multi-criteria and not solely on regression.
- Considered as a strategy for minimizing the regression of skill, thus shortening the time needed to gain back the same level of skill proficiency that existed at the end of the school year.
- Deliverable in a variety of environments and structures such as: (a) Home with the caregiver teaching, and staff consulting (b) School based (c) School based with community activities (d) Related services alone or in tandem with the above.
Extended School Year (ESY) IS NOT:
- A mandated 12-month service for all students with disabilities.
- Required for the convenience of the school or caregivers and, therefore, cannot serve as a day care or respite care service.
- Necessary to continue instruction on all of the previous year’s IEP goals during the ESY period; rather, the focus should be on those specific, critical skills where regression, due to an extended vacation period, may occur.
- Considered to help students with disabilities advance in relation to their peers.
- For those students with disabilities who exhibit regression solely related to medical problems resulting in degeneration or transitional life situations such as divorce or death of a family member. This type of regression is not due to the interruption of summer vacation.
- Required solely when a child fails to achieve IEP goals and objectives during the school year.
- Intended to provide a child with education beyond that is prescribed in his/her IEP goals and objectives.
- Summer School. ESY is distinct from traditional summer school, tailored to prevent regression in acquired skills for students with disabilities. Unlike summer school, ESY focuses on maintaining and reinforcing skills rather than addressing missed academic goals.
- Designed to provide compensatory services. These services should be separate from ESY and provided in an alternative setting.
Understanding the ESY and its distinct role in supporting students with disabilities is essential for caregivers navigating the special education landscape. Active participation in the IEP process, clarity regarding the distinction between ESY and compensatory services, and awareness of what ESY should and should not provide empower caregivers to advocate effectively for their child’s comprehensive educational needs.
