As a parent and advocate, I understand that navigating the Individualized Education Program (IEP) process can be overwhelming for parents new to this journey. An important aspect to understand is the distinction between accommodations and modifications in the school system. These two terms play a crucial role in ensuring that students with disabilities or special needs have the opportunity to succeed in the classroom alongside their peers. Let’s delve into the key differences between accommodations and modifications, their significance, and how they can be used to support your child’s learning experience.
What Are Accommodations and Modifications?
Accommodations and modifications are educational tools that support students with diverse learning needs. These provisions are outlined within an Individualized Education Program (IEP) to address the unique requirements of a student and ensure they can access the curriculum in a manner tailored to their abilities.
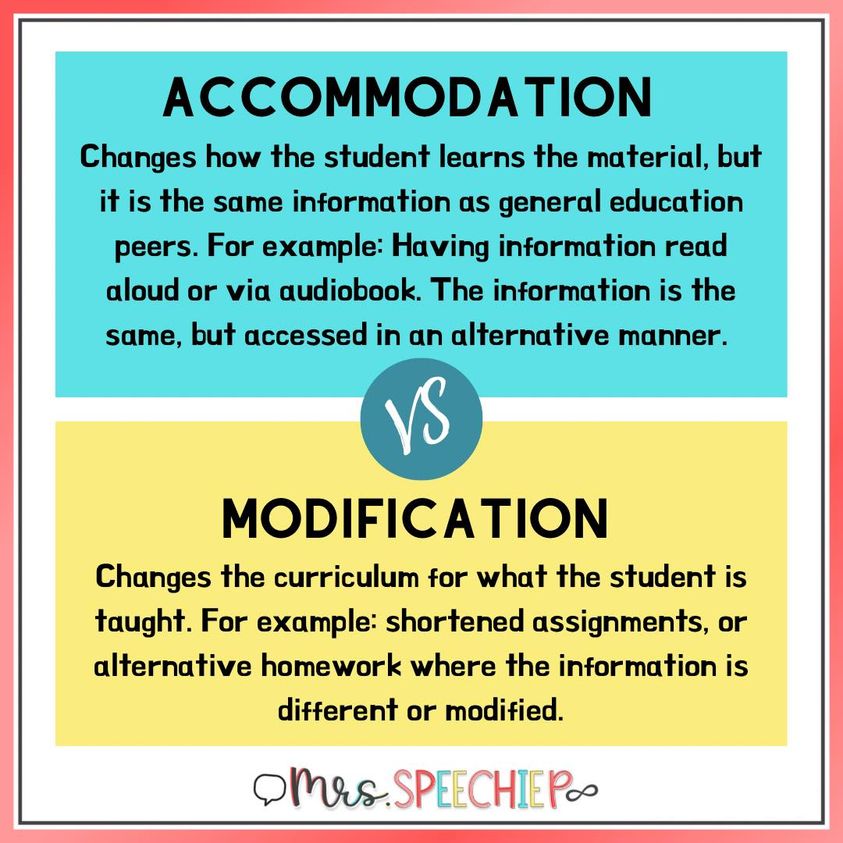
Accommodations change how a student learns the curriculum. Modifications change the curriculum to fit the learner.
Accommodations refer to adjustments made in how a student accesses learning materials and information. These alterations do not change the content or the academic expectations; instead, they modify how the information is presented or assessed. The primary goal of accommodations is to level the playing field, allowing students with disabilities or special needs to participate in the same curriculum as their peers, but in a way that caters to their individual learning styles.
Examples of accommodations include:
- Extended time for completing assignments or tests
- Preferential seating to aid focus and attention
- Providing study guides or outlines to help with organization
- Using assistive technologies, like text-to-speech software or calculators
- Offering breaks during challenging tasks to avoid sensory overload
Modifications:
On the other hand, modifications involve making alterations to the curriculum itself to suit the student’s learning capabilities. Unlike accommodations, modifications adjust the expectations of what a student is required to learn. These changes are appropriate for students who may be significantly below grade level in certain subjects or have unique learning goals that differ from their peers. Modifications can result in your student receiving a degree other than the typical high school diploma, as the curriculum has been changed.
Examples of modifications include:
- Simplifying reading materials to match the student’s reading level
- Reducing the number of math problems to complete in a given assignment
- Adjusting the grading criteria to focus on specific learning objectives
- Substituting certain assignments with alternatives that align with the student’s abilities
Understanding the distinction between accommodations and modifications is important for parents navigating the IEP process. Accommodations are designed to provide support to students, allowing them to access the standard curriculum while addressing their individual learning needs. Modifications, on the other hand, involve altering the curriculum to meet the student at their current level of academic functioning.
By collaborating with teachers and actively participating in the IEP process, parents can play a pivotal role in ensuring their child receives the appropriate support to thrive academically and personally. Let’s work together to create an inclusive educational environment where all students have the opportunity to succeed and reach their full potential.